Learning Objectives:
-
State and describe common Java terms.
-
State what needs to be installed to write, compile and run a Java program.
Software
-
Computer instructions or data.
-
Makes a computer do something and are written to run on the hardware.

-
Software is usually written in a high level language which is fairly similar to our own spoken languages.
-
This makes it easier for us humans to use.
-
However, computers only understand machine code which is in binary form(1s and 0s).

Compilers
-
Translate high level languages (the translator's source code) into machine code (the translator's object code) which can be executed by a computer.
-
Makes a computer do something and are written to run on the hardware.
Java Compiler

Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
-
Executes the Java Bytecode(.class file)produced by Javac Compiler.
-
Each Operating System (OS) e.g. Windows, Mac, Linux etc... has a different JVM to tell the OS what to do in its own machine code language.
-
This is why we call Java a platform (OS) independent language.
-
As any OS can execute a Java program as long as it has a Javac Compiler or it has previously been compiled into Java Bytecode and it has a JVM to execute this Java Bytecode.
-
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
-
Includes:
-
When you have JRE installed on your system, you can run a Java program however you wouldn't be able to compile a Java program.
-
So just installing JRE is only sufficient if you only wish to run Java programs(but not compile them).
Java Development Kit (JDK)
-
Includes:
-
In order to create, compile and run Java programs you will need JDK installed on your computer.
Using a text editor & the command prompt Vs IDEs
-
Although it is possible to use IDEs like Eclipse or online ones like Jdoodle, I will start with using a text editor and the command prompt and later introduce the online IDE Jdoodle.
-
I consider:
-
Using a text editor and the command prompt to be the most basic and "authentic" way of programming and it forces students to learn correct syntax because it offers no support.
- However, some teachers argue that the fact that there is no support, makes this the most difficult way to start programming.
-
IDEs like Eclipse too cumbersome and unnecessarily overcomplicated to use in AP CS.
-
- However, because programming with a text editor and the command prompt takes longer than using IDEs and correct syntax is not strictly necessary in the final exam, I will introduce the online IDE Jdoodle soon.
-
Install Java
-
You can get Java 8 from Oracle(the developers of Java, but note that you will have to register with them)or more simply from the "General Information" section of my AP CS page(no registration required).
- Remember you need to install the JDK.
-
Recommended: install only the latest version of "8u...". Later versions (11, 12, ..) are not needed and overcomplicate things for AP CS. Also, although it is possible to install multiple versions of JDK/JRE concurrently, it is messy.
-
So if you have previous installations of other version(s)of JDK/JRE, I suggest you un-install ALL of them.
- Search Windows for "Control Panel" -> "Programs" -> "Programs and Features" -> Un-install ALL programs begin with "Java", such as "Java SE Development Kit ...", "Java SE Runtime ...", "Java X Update ...", etc.
- I suggest that you click the back and forward arrows each time you uninstall to make sure you update the installed programs list.
-
- If necessary, read "JDK Installation Common Errors".
For how to proceed on a Mac please see here and
note that the steps below are uneccessary for a mac.
Permanent Java path setup guide
The following steps are for Windows PCs and before 1st time use only
(only once)
.
- The Java compiler javac.exe and Java runtime java.exe reside in the "bin" folder of the JDK folder.
- So to run JDK programs from the command prompt, it needs to be told to also search this folder for executable programs.
- This is done by adding this "bin" folder to what is known as the "Path".
- Navigate to the folder which contains the JDK's programs and click the yellow folder icon in the address bar.
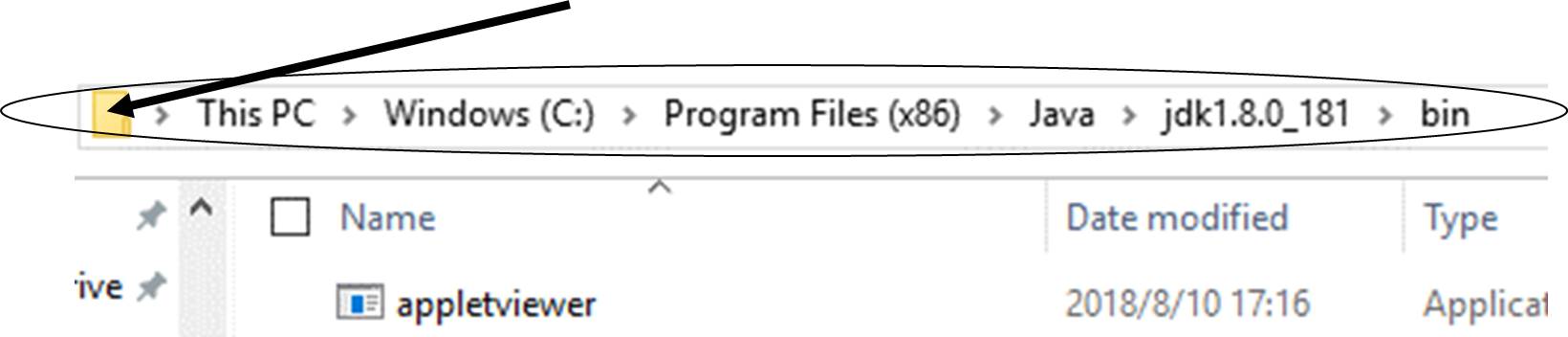
- Copy the address for pasting later.
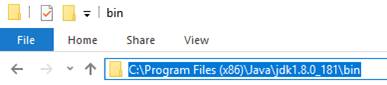
-
Search and start typing "environment variables"(you won't have to type the whole phrase)and click "Edit the system environment variables".
-
If you are using an older version of Windows or for whatever reason cannot do this, please complete step 4 below, otherwise skip to step 5.
-
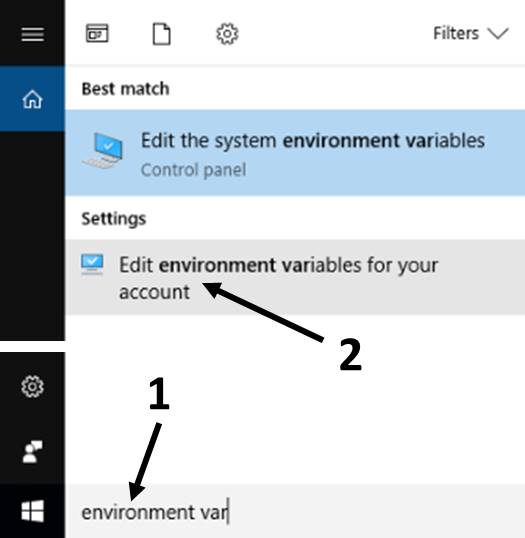
-
If you cannot do step 3 above only use the Control Panel(Start Menu - Windows System).
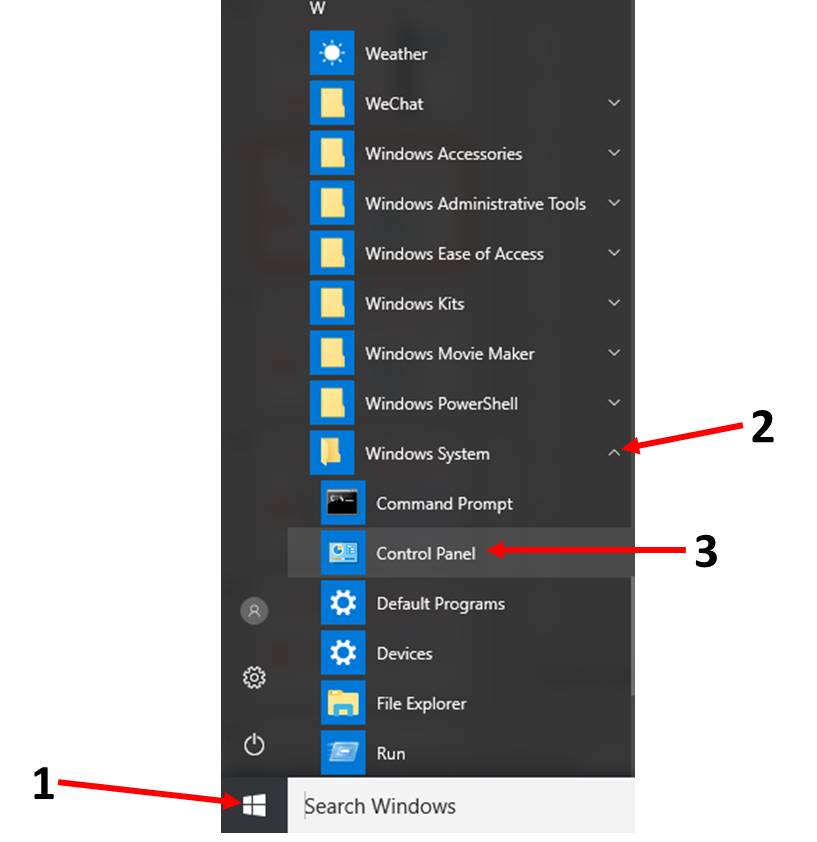
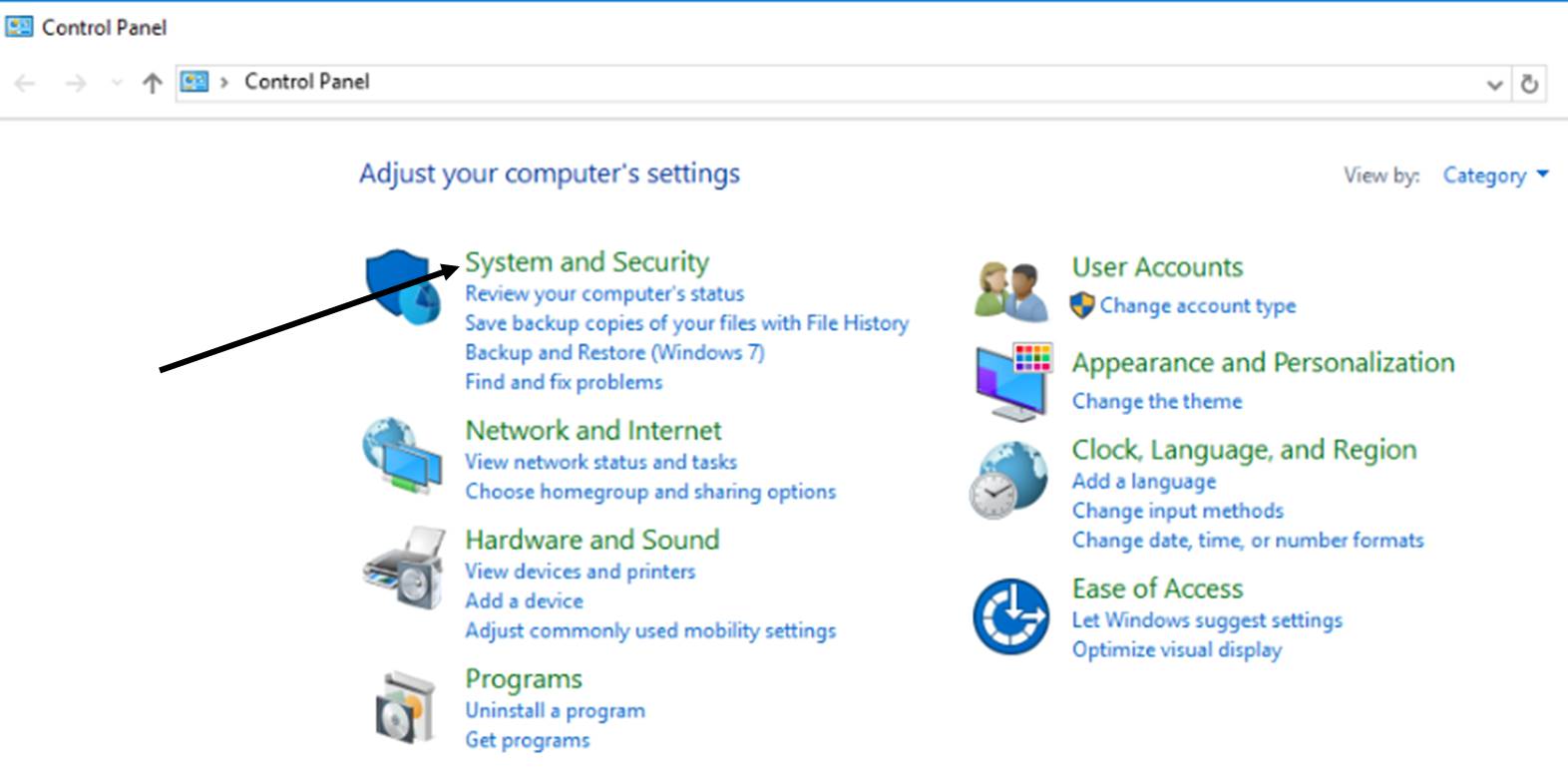
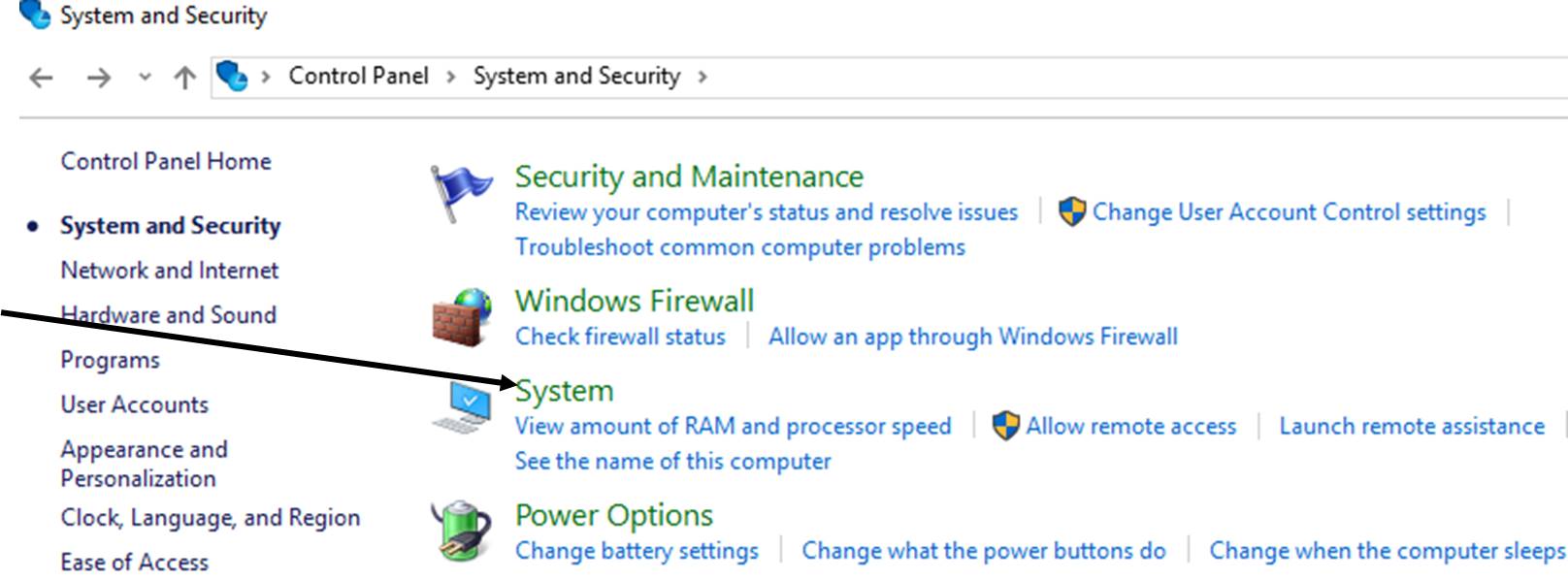
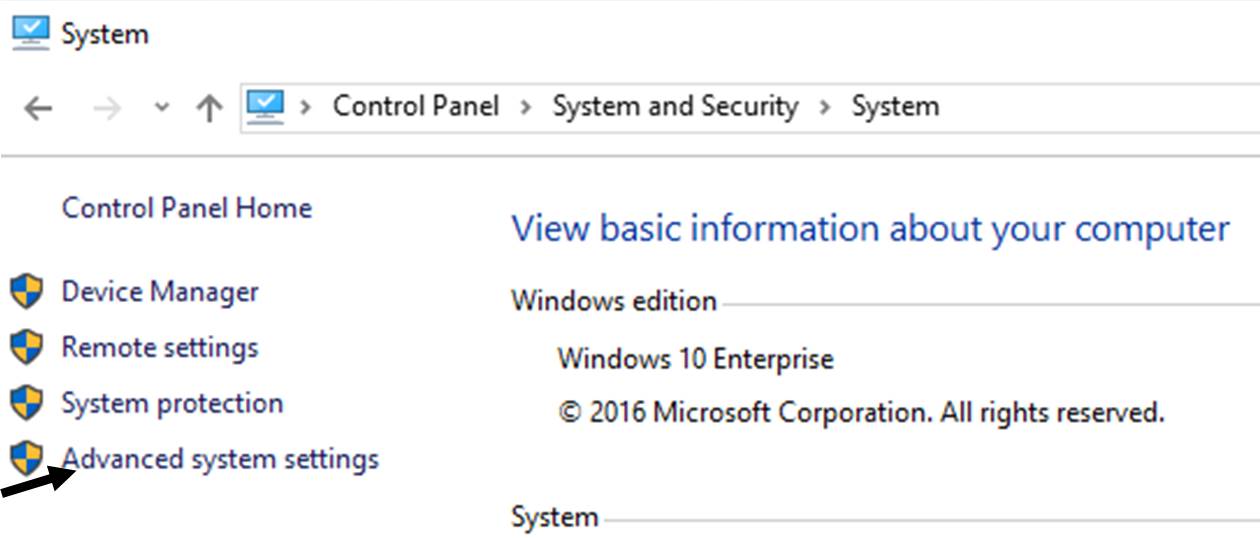
-
"Advanced" -> "Environment Variables"
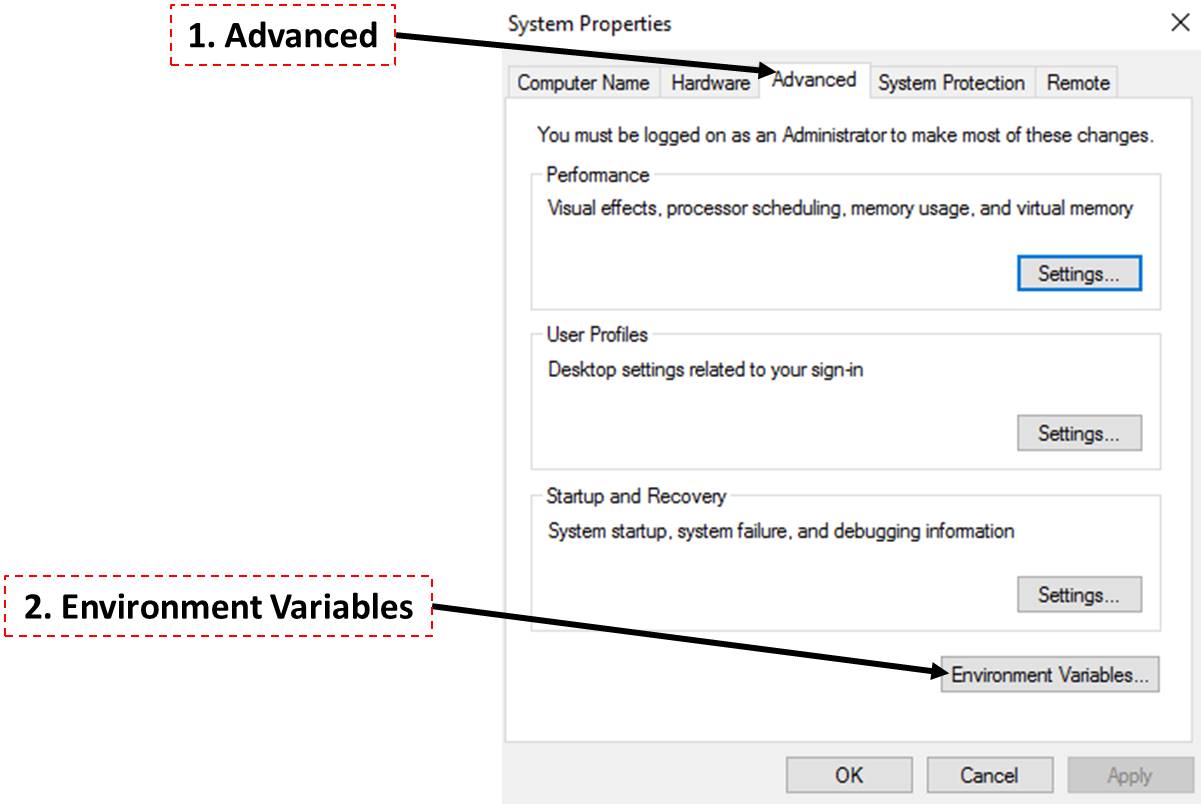
-
Click "Path" and "Edit".
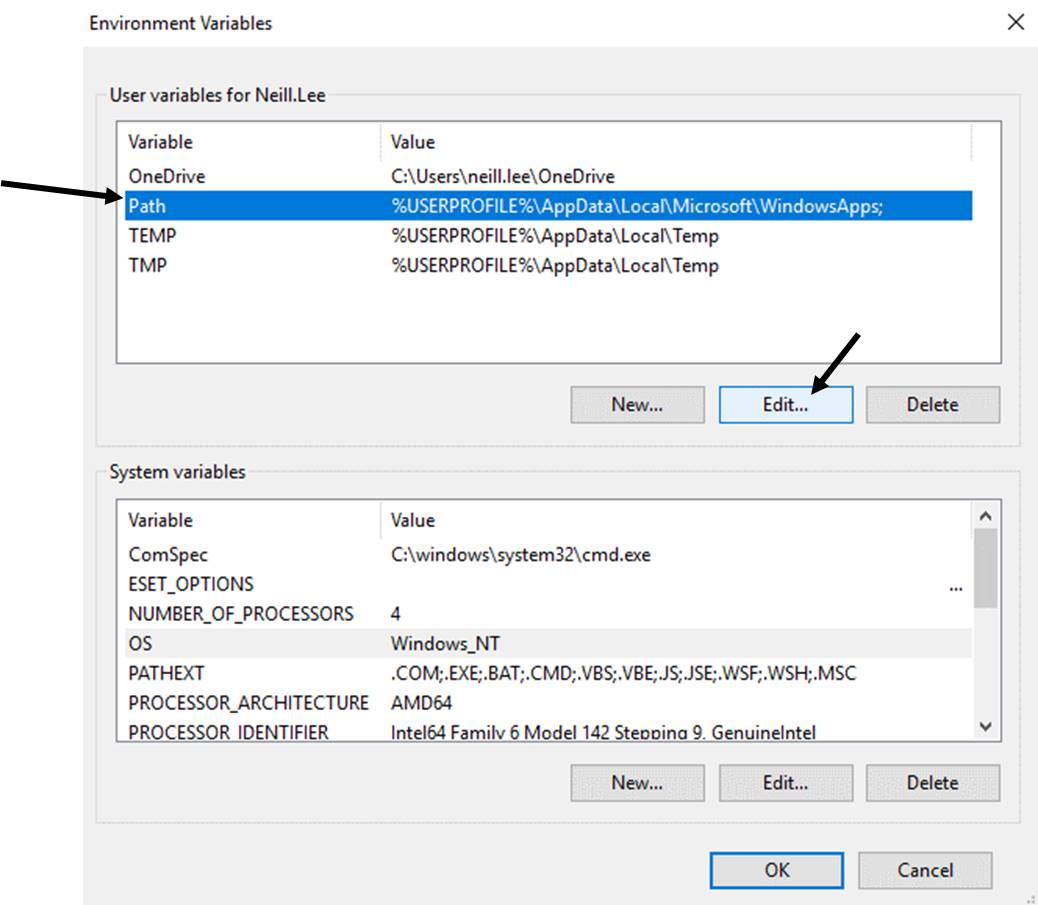
-
Read the following 3* before actually completing as there is no undo!
-
If you do not see the screenshot below skip to part (b).
-
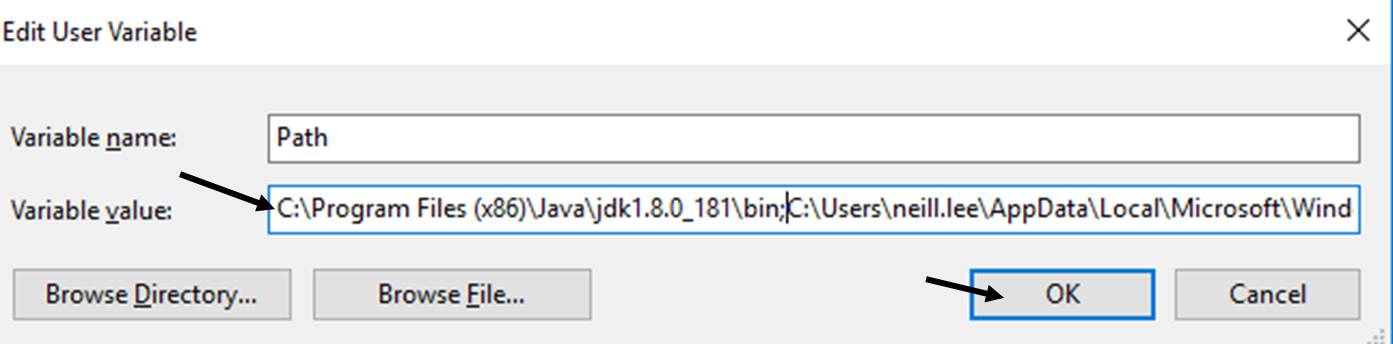
-
Do NOT delete "Variable value" field.
-
Otherwise, some existing applications may not run.
-
To be SAFE, copy the content of the "Variable value" and paste to somewhere before changing it!!!
-
-
-
Click at the beginning of the existing contents to get a cursor and paste the address that you copied earlier(Ctrl + v), of the "bin" folder, followed by a ;
-
Click OK * 2(this & the previous "Environment Variables" windows).
END
-
Only complete this step if you don't see the screenshot in part (a) above. Click "New" and click in the next empty box, paste the address that you copied earlier(Ctrl + v), of the "bin" folder. Then click OK * 2(this & the previous "Environment Variables" windows).
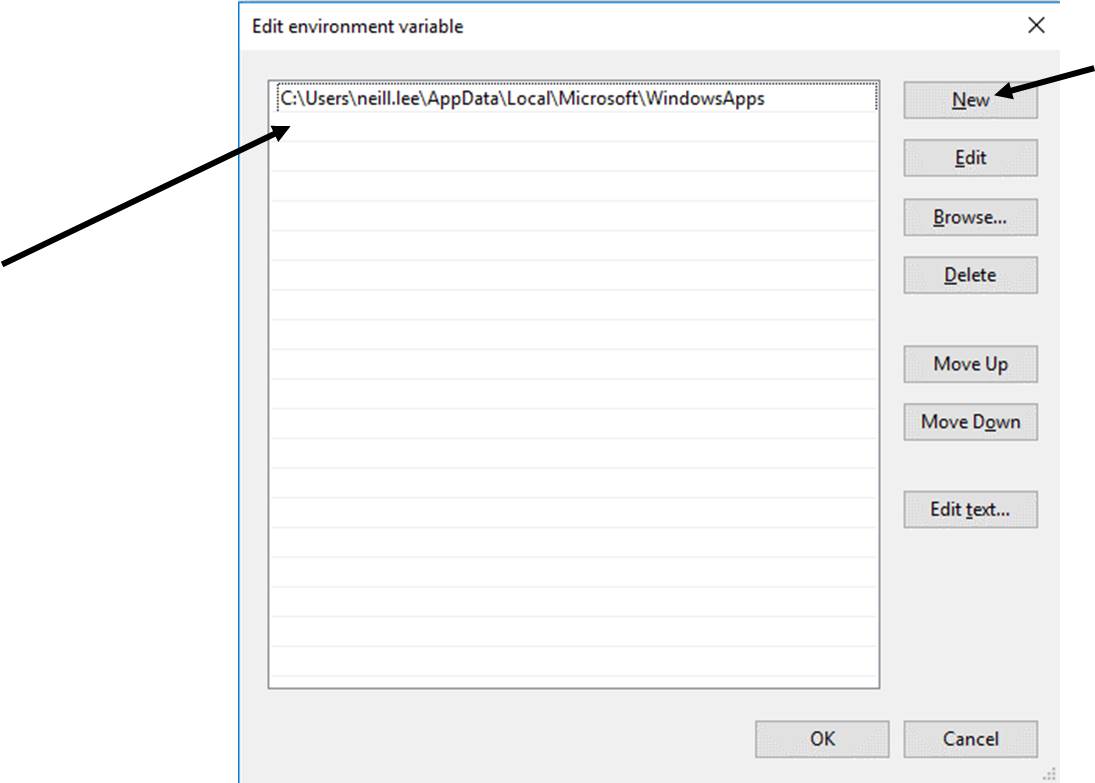
END
